The demand for all-natural, long-lasting dog chews made from Himalayan yak milk (“chhurpi”) has experienced significant growth in recent years. As a certified exporter in Nepal, we’ve seen the U.S. importers are actively seeking these premium pet treats. Nepal’s dog chew exports reached a record NPR 4.0 billion (over $27 million) in 2024–25, with approximately 90% destined for the U.S. market. In the first half of 2025, Nepal exported 963 tonnes of yak chews valued at NPR 1.80 billion, with 852 tonnes (NPR 1.59 billion) imported by the United States.
According to Dr. Ramnand Tiwari of Nepal’s Department of Livestock Services, “Nepal’s dog chews are emerging as a premium export in the global pet treat market, fueled by rising demand in the United States and beyond.” American and Canadian pet owners demonstrate a strong preference for hard cheese-based chews made from yak milk, primarily produced in eastern Nepal. This comprehensive guide provides the U.S. importers with detailed procedures for importing Himalayan dog chews into the United States, covering regulatory compliance, supplier certification requirements, and operational best practices.
Why the US is a Prime Market?
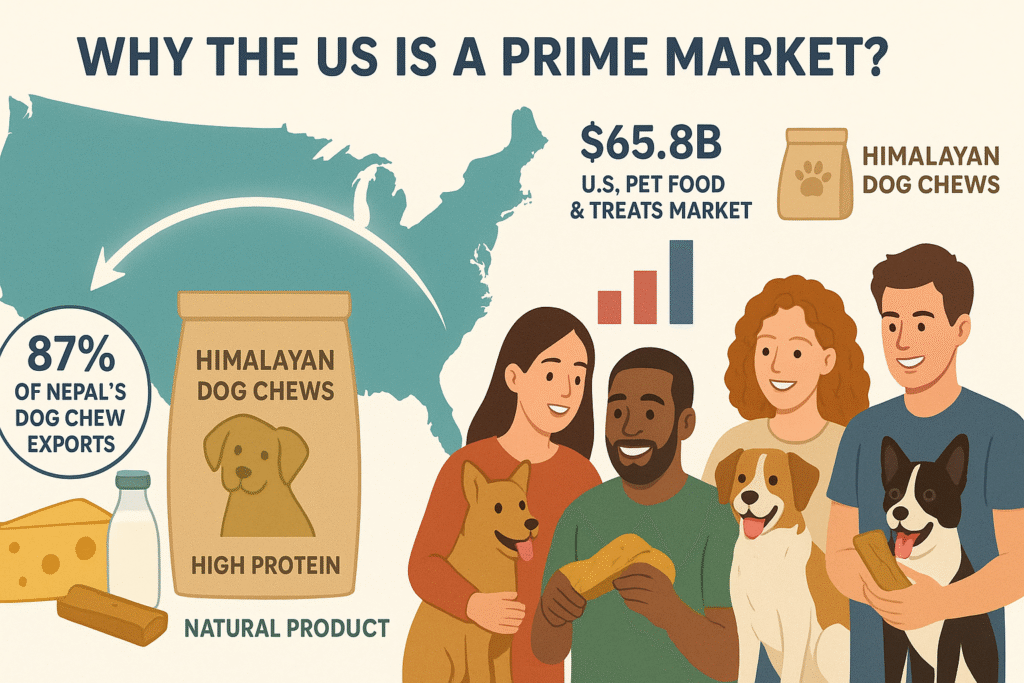
The United States represents the largest market for Himalayan dog chews. About 87% of Nepal’s dog chew exports go to the U.S. According to rising nepal daily news, In mid-2025 Nepal shipped 1,888 tonnes (NPR 3.49 billion) of chhurpi to the U.S. buyers, compared to 138 tonnes (NPR 308 million) to Canada. Industry officials attribute this dominance to strong the U.S. consumer demand for natural, high-protein pet treats and Nepal’s established reputation for quality manufacturing.
The U.S. pet industry represents a substantial and expanding market. According to the American Pet Products Association, the U.S. consumers spent $65.8 billion on pet food and treats in 2024, with the pet treats and chews segment representing an $11–13 billion market. In recent years pet owners have shifted toward healthier, limited-ingredient Products. A 2022 Packaged Facts survey revealed that 83% of the U.S. pet owners prefer healthier treat options.
Himalayan yak chews align with these market trends, consisting of 99% yak-and-cow milk cheese with high protein and mineral content, containing only salt and lime as additives. For dog-centric households (68 million U.S. homes have dogs), premium natural chews represent a desirable product category. The robust U.S. import market presents opportunities for emerging importers to establish private label “Himalayan Dog Chew” product lines.
Regulatory & Compliance Requirements in The US
Federal Regulatory Requirements
Importing pet treats, including Himalayan yak chews, into the United States requires strict adherence to federal food and agricultural regulations. Key regulatory frameworks include:
- Pet Food Uniform Regulatory Reform (PURR) Act (2024): This newly-introduced federal legislation centralizes pet food label and ingredient approvals under the FDA authority, replacing inconsistent state-by-state oversight. While importers should monitor this Act’s implementation, it does not modify existing safety standards but rather streamlines label approval processes across states.
- FDA/Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (FD&C Act): All pet foods and treats are governed by the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (FD&C Act). Under Sections 402–403 of the FD&C Act, imported animal foods must be safe and wholesome, contain no harmful substances, and be truthfully labeled. U.S. regulations (21 CFR Part 501) specify labeling rules: each package must show a product name, species (dog/cat), net weight, ingredients (using AAFCO names), guaranteed analysis (min protein/fat, max fiber/moisture), feeding directions, and the name/address of manufacturer or importer. Importers should check that their supplier’s labels meet these federal rules before shipping.
- Public Health Security and Bioterrorism Preparedness and Response Act (2002): The U.S. law requires facility registration and prior notice for all imported foods (including animal foods). The foreign manufacturer/processor must be registered with the FDA, and the importer must file an electronic Prior Notice (via FDA’s FURLS) at least 2 hours (or more, depending on transport mode) before arrival. Each import shipment of yak chews must have this notice on file. Failure to register or file Prior Notice can result in the shipment being refused by the FDA. (Note: FDA allows foreign firms to obtain a unique facility identifier to streamline this process.)
- Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA): FSMA gives the FDA authority for proactive safety programs. In particular, FSMA’s Foreign Supplier Verification Program (FSVP) requires the U.S. importers to implement a written program verifying that their Nepalese suppliers meet the U.S. safety standards. This means conducting hazard analysis, ensuring traceability, and verifying the exporter (and their production controls) are reputable and compliant.
- USDA/APHIS Permits: Because yak chew is an animal-origin product (dairy cheese), USDA’s Animal and Plant Health Inspection Service (APHIS) may require an import permit. Generally, a USDA import permit is needed for any animal food containing meat or dairy from countries with certain livestock diseases. Nepal is considered a foot-and-mouth risk country, so importers should apply via APHIS VSS (Veterinary Services) eFile for an import permit before shipping. Even if not explicitly required, having an APHIS permit and the accompanying Health Certificate (from Nepal’s animal health authorities) can streamline Customs entry and USDA inspection.
- Other Federal Rules: Other FSMA rules (such as Sanitary Transport and preventive controls) may apply once products arrive. Importers must ensure shipments use sanitary transportation and follow any FSMA ‘Current Good Manufacturing Practices’ in production.
FDA (safety, labeling, registration, prior notice, FSVP), USDA/APHIS (import permits for dairy), and the Bioterrorism Act. Importers should work with their Nepalese exporter to gather all required export health and safety certificates, and register or notify FDA as needed. A licensed customs broker can also guide the filing of documents with CBP.
Essential Certifications and Quality Standards
The U.S. buyers expect Nepalese yak chew suppliers to meet international quality benchmarks. Top exporters typically hold:
- ISO Certifications: (e.g. , ISO 22000 Food Safety, ISO 9001 Quality Management) ensure robust food safety management systems.
- HACCP: A validated Hazard Analysis & Critical Control Points plan for dairy processing is often mandatory.
- DFTQC Standards: Nepal’s Department of Food Technology & Quality Control (DFTQC, under the Ministry of Agriculture) sets local hygiene and testing standards. Exporters should pass DFTQC inspections and obtain an export “Test Report” confirming microbial and contaminant limits.
In fact, leading Nepali firms highlight exactly these credentials: “Our current certifications include FDA approval, ISO, HACCP, SA8000 and DFTQC standards”. (Note: the FDA doesn’t “approve” pet foods per se, but foreign facilities must register and comply with the FDA rules.) Strong quality systems give the U.S. importers confidence – ask potential suppliers for copies of their certificates and audit reports. Also, verify they use only approved ingredients (all components of chhurpi should be GRAS or AAFCO-listed). A Nepal exporter certified by ISO, HACCP, and SA8000 is more likely to meet the U.S. scrutiny.
Labeling and Packaging Standards
The U.S. law mandates specific label content and packaging to ensure safe, clear pet food products. Essential label elements include the brand and product name, intended species (Dog), net weight (in lbs/kg), ingredients list, guaranteed analysis (protein, fat, fiber, moisture), feeding directions, and the name and address of the manufacturer or distributor. Many importers also include feeding guidelines (serving size) and calorie content. Labels must use AAFCO-defined ingredient names and display nutrition guarantees in the prescribed order. (For example, “Guaranteed Analysis: Crude Protein (Min) 50%, Crude Fat (Min) 30%, Crude Fiber (Max) 1%, Moisture (Max) 10%.”) All numeric values need both the U.S. and metric units; net weight must be on the principal display panel.

Packaging must protect the chews and control moisture. Himalayan yak chews typically have ~10–12% moisture and can mold if damp. Use vacuum-sealed or high-barrier pouches with moisture-absorbing liners or desiccant to keep products dry. Resealable pouches or bags with zip closures help consumers keep chews fresh. Insert a silica gel or oxygen absorber for bulk shipments to prevent spoilage over long transit. Durable corrugated cartons with tamper-evident seals (and USDA-inspected dairy labeling) are recommended for sea shipments. The packaging should also include handling instructions (e.g. , “Store in a cool, dry place”) to maintain quality.
For larger wholesale orders, palletize cartons on wooden pallets and wrap them in plastic to protect from moisture. As one Nepalese exporter advises, attach clear carton labels on each box to avoid confusion at unpacking. In summary, ensure all federal labeling requirements are met (21 CFR 501 and AAFCO guidelines) and that the packaging preserves chew quality (moisture-barrier materials, desiccants, and secure sealing).
Step-by-Step Import Process of Himalayan Yak Chew
Bringing Himalayan yak chews into the U.S. involves coordinated steps between the Nepal exporter and the U.S. importer:
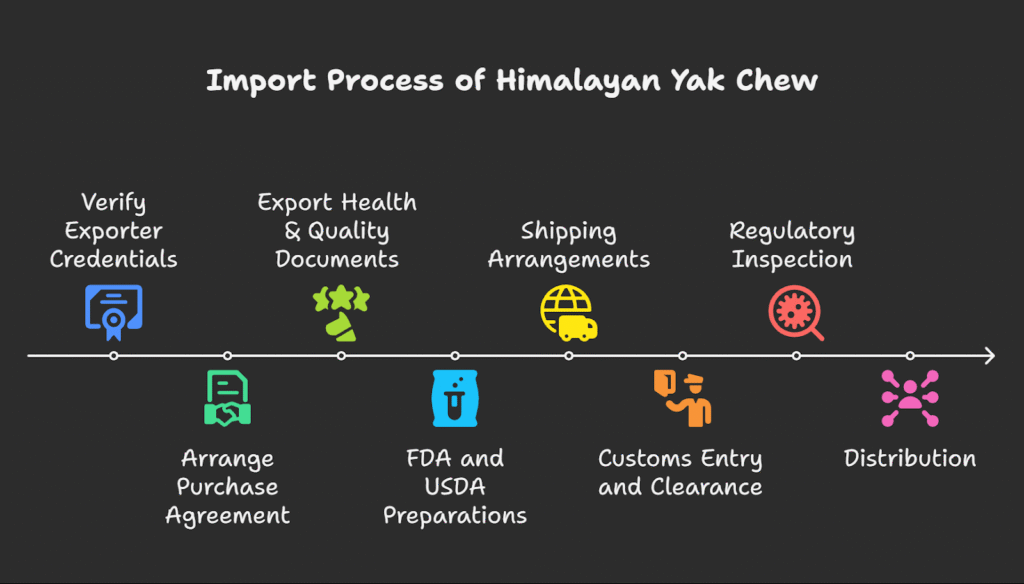
- Verify Exporter Credentials: Confirm your Nepalese supplier has all necessary certifications (ISO, HACCP, DFTQC export number, etc.) and experience exporting pet treats. Ensure they register their facility with the FDA (Foreign Facility Registration) and have a Nepal government Veterinary Sanitary Certificate for the dairy product.
- Arrange a Purchase Agreement: Sign a proforma invoice specifying product details, Incoterms (e.g. , FOB Kathmandu), prices, and required documents (COO, test reports).
- Export Health & Quality Documents: The exporter obtains:
- DFTQC Test Report: Government quality control certificate attesting product safety (often tested by Nepal’s FDA or NPHL).
- Veterinary Health Certificate: From Nepal’s livestock services, certifying hygienic production of dairy chews.
- Certificate of Origin (C/O): Issued by Nepal’s Chamber of Commerce.
- GSP Certificate (if applicable): For preferential tariff access under the U.S. trade programs (if Nepal qualifies).
- Packing List: Detailing cartons, weight, and products.
- Commercial Invoice: Itemized sale invoice.
- DFTQC Test Report: Government quality control certificate attesting product safety (often tested by Nepal’s FDA or NPHL).
- FDA and USDA Preparations: As the U.S. importer, register your importing facility with the FDA’s FURLS system and obtain a Facility Identifier (UID). Enroll and submit Prior Notice through the FDA’s PREDICT system at least 2 hours (air) or 4 hours (sea) before arrival. Apply for any required USDA APHIS VS import permit (for dairy-based pet food). Coordinate with the exporter to ensure they include the APHIS permit number on shipping documents.
- Shipping Arrangements: Book freight (air or ocean) with a reliable carrier that can handle perishable pet foods. For sea shipments, use a temperature-controlled container if possible (15–21 °C) and include moisture controls. For urgent smaller loads, air freight is faster. Label all cartons clearly with handling and content information.
- Customs Entry and Clearance: Upon arrival at the U.S. port of entry, a licensed customs broker submits entry documents to CBP and FDA on your behalf. This includes the entry summary, invoice, packing list, COO, health/test certificates, prior notice confirmation, and APHIS permit. Remember to file the customs entry (CBP Form 3461/7501) within 5 working days of arrival. Pay any applicable duties or fees. Although most pet foods under HS 23091000 are duty-free, you must still file the entry.
- Regulatory Inspection: FDA or USDA may inspect the shipment. They will review labels and may take samples for lab testing (microbiological or chemical). Products not meeting standards can be detained or refused. To avoid this, supply complete certificates of analysis (COAs) and ensure testing is done by accredited labs before shipping.
- Distribution: Once cleared, the chews can be warehoused or distributed to retailers. Maintain records of safety tests and supplier audits for FSMA compliance. Continually communicate with the Nepali exporter about any feedback or issues.
This step-by-step process must be meticulously followed. Working with experienced customs brokers and a reliable freight forwarder can ensure documents (like FDA prior notice, APHIS permit, and CBP entry) are submitted correctly and on time.
Shipping and Logistics
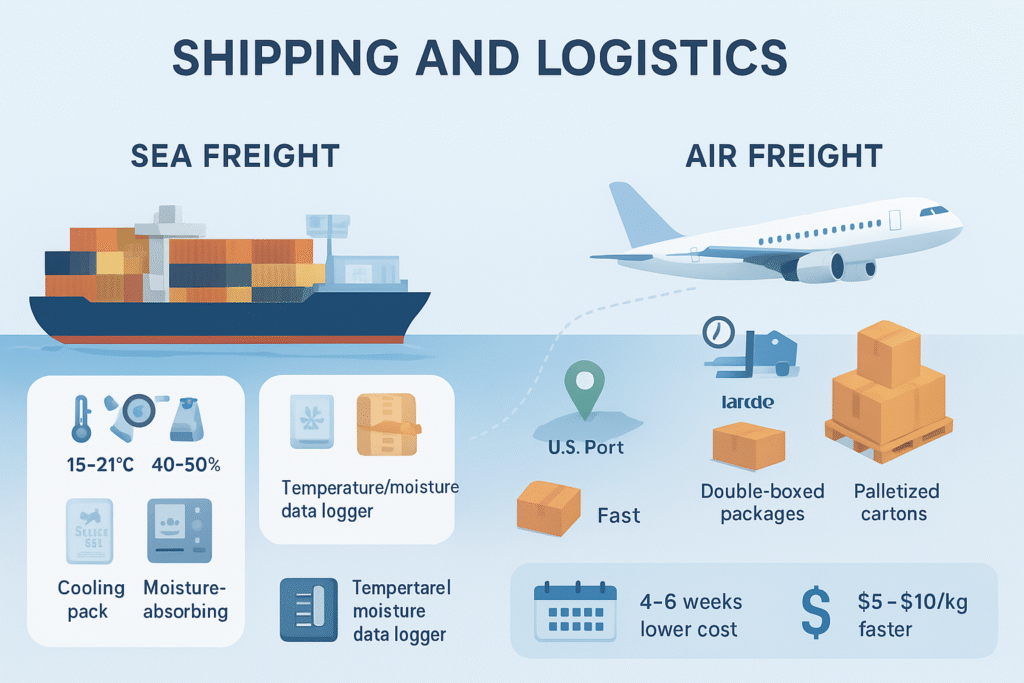
Choosing the right shipping method and maintaining product integrity is crucial. Sea Freight: Best for large orders (over ~8000 kg). Use a refrigerated container (reefer) or dry container with cooling packs. Set the temperature around 15–21 °C and the humidity to 40–50%. Include moisture-absorbing materials inside cartons (silica gel or clay packets) to prevent mold. Seal pallets in humidity-resistant wrap. Attach temperature/moisture data loggers in the container. Ensure a tracking number is available to share with the importer for real-time updates.
Air Freight: Ideal for smaller, urgent shipments. Air transit is faster (1–3 days), but more expensive per kg. Ensure packages are well-protected (e.g. , double-boxed) and palletized if multiple cartons. Ship in sturdy plastic or corrugated boxes to withstand handling. Air cargo facilities at major U.S. airports have refrigeration, but temperature control may still fluctuate. Shipments by air should still include desiccants and thermal insulation.
Cost Considerations: Sea freight from Kathmandu (via India/Mombasa routes) to a West Coast port may be cheaper per kilo but slower (4–6 weeks). Air freight (e.g. , Kathmandu–San Francisco) costs ~$5–$10 per kg (depending on route and fuel). Factor in insurance to cover spoilage risk.
Best Practices:
- Consolidation: For small importers, consolidate orders with others to fill a container.
- Tracking: Always get airway bill (AWB) or bill of lading (B/L) numbers and monitor schedules.
- Warehouse Prep: The U.S. warehouse should be cool/dry. Offer importer guidelines for unpacking and storing chews (e.g. , keep sealed until distribution).
According to the U.S. import experts, investing in temperature-controlled shipping is “most cost-effective on larger shipments,” while “air freight is the best option” for smaller loads. In all cases, proper packaging (strong boxes, pallets, stretch wrap) and clear labeling help avoid damage, delays, or misrouting during transit.
Common Mistakes to Avoid

Even minor oversights can derail an import. Common pitfalls include:
- Missing Documentation: Failing to provide an FDA registration number, Prior Notice confirmation, or APHIS permit can cause rejection. Likewise, omitting the Exporter’s DFTQC or sanitary certificates or the Certificate of Origin will delay customs. Always double-check that all paperwork accompanies the shipment.
- Incorrect Labeling: Labels with incorrect or incomplete info – for example, listing nutrition values on a dry matter basis instead of as packaged, or lacking nutrient analysis – will violate FDA rules. Mislabeling the product name (e.g. , “cheese chew” vs. “dog chew”) or species can lead to refusals.
- Ingredient Issues: Using any unapproved additives or carrying residues of illegal pesticides can trigger detention. All ingredients must be FDA-approved for animal feed. Some importers neglect to check the Nepal facility’s cleaning records or misidentify a component.
- Tests and Contaminants: Underestimating testing requirements can be costly. U.S. authorities may test for heavy metals, mycotoxins, or pathogens. Skipping pre-export lab checks (microbiological and chemical) can result in a failed sample at the U.S. border. Accredited labs charge a few hundred dollars per sample for nutritional/contaminant analysis, but failing a U.S. test could destroy a shipment.
- Poor Packaging: Using thin or non-barrier film can lead to moisture ingress and mold. Not securing pallets can cause crushed boxes. Some importers receive shipments with collapsed cartons because the pallet wrap was inadequate. Always invest in quality packaging and clearly label cartons as “Handle with Care – Fragile Food.”
- Tariff Misclassification: Assigning the wrong HTS code can lead to unexpected duties or fines. Himalayan dog chews should fall under HS 2309.10.00 (Prepared animal feed), which is generally duty-free. Classifying them under a chemical or non-food code, for example, would be a costly error.
By planning ahead and enlisting knowledgeable partners (freight forwarders, brokers, legal counsel), you can avoid these mistakes and ensure a smooth import.
Estimated Costs and Tariffs
Importing involves various costs beyond the product price. Customs Duty: Himalayan yak chews (HS 2309.10.00) are typically duty-free. (A 2002 U.S. Customs ruling explicitly classified dog chews under 2309.10.0090 and stated “the rate of duty will be free”.) Even without duty, the importer pays a Merchandise Processing Fee (MPF) (~0.3464% of shipment value, min $32) and any harbor maintenance fees.
Freight: Sea freight can cost roughly $2–$5 per kg (depending on volume), while air freight is usually $5–$15 per kg. For example, a 1000 kg air shipment might run $10,000–$15,000 round trip. Reefers cost more, plus any container rental fees. Insurance is typically 0.3–0.5% of cargo value.
Testing and Compliance: Lab tests (nutritional analysis, contaminants) generally range from $200–$800 per batch. For example, one U.S. lab’s fee schedule lists a basic pet food nutrient analysis at $325. If heavy-metal screens or microbial analyses are needed, each can add a few hundred dollars. Factor in costs for Certificate of Analysis (COA) documentation and any special assays.
Certifications & Audits: If the U.S. partner requires third-party audits (e.g. , USDA Organic, SQF), budget those fees too ($5k–$15k per audit). Even without them, having current certificates (ISO, HACCP) can increase supplier costs.
Example: A full import of 1 tonne (1000 kg) of yak chews from Nepal (at $13-14/kg FOB) might incur:
- FOB product: $13,500 average
- Air freight & insurance: $3000
- Sea Shipping in a container for 10000-25000 kg: $1 to $0.6/kg
- Customs broker & MPF: $300
- FDA Prior Notice (free online) + minimal paperwork fees: negligible
- Testing (microbial + nutrients): $neglibale
- Packaging (export cartons, pallets): Done by Exporter
- Misc (importer handling, pallet fees): $200
- Total ~$16500, or $16.5 – $17/kg CIF (Cost, Insurance, Freight) before markup.
Total cost by bulk purchases by Sea shipping for 10000-25000 kgs will be like $13.5-14/kg.
Keeping accurate HTS codes and being aware of U.S. import costs helps in pricing. Since chews under 23091000 are duty-free, the biggest variable is shipping and testing.
Working with Customs Brokers and Testing Labs
Partnering with experts can save headaches. A U.S. customs broker will handle entry filing (CBP and FDA forms) and clarify any tariff or bond requirements. In fact, pet food requires a customs bond even for shipments under $2,500. Brokers ensure your paperwork is complete, classifications (HS codes) are correct, and duties/fees are paid. Their advice can prevent costly mistakes: as one customs firm notes, importers of regulated goods “should work with a professional customs broker… to avoid costly mistakes”.
For quality testing, work with accredited food labs familiar with FDA animal feed regulations. Many labs offer pet-food panels including nutrient profiles and contaminant screens. For example, NutriData lists a pet food analysis at ~$325 covering protein, moisture, fiber, and fat. Additional tests (e.g. , Salmonella, E. coli, aflatoxins) may add $50–$200 each. Some importers also send samples to USDA-approved labs for veterinary screening. Keep laboratory reports on file for FDA or APHIS audits.
Engage the broker early: they can advise on AMS pesticide tests (if required) and verify that labels meet state and federal law. Likewise, a lab consultant can guide sample collection at the Nepal factory so shipments meet U.S. microbiological standards. Using these professionals streamlines compliance and reduces the risk of detention at the border.
Market Opportunities and Private Label Options
The high U.S. demand and the uniqueness of Himalayan chews offer branding opportunities. Many U.S. pet food companies import yak chews as private-label or white-label products. For example, one Nepali exporter noted that Manaram Group ships around 100 tonnes/month of chhurpi to the U.S. for repackaging under the “Himalayan Dog Chew” brand. Smaller U.S. pet startups often purchase generic yak chews and label them with their own branding and story about Himalayan origins.
Five years of government data tell the story: according to NepYork/Nepal Dept. of Customs: Nepal chhurpi exports surged 240% in five years, from NPR 1.22 billion (2019–20) to NPR 4.5 billion (2024–25), Nepal’s dog chew export sector has grown approximately 240% in five years, making it one of the fastest-growing agricultural export categories in the country. The Himalayan origin story itself is a selling point. According to industry sources, savvy brands “tell your story” on packaging – e.g. , “made at 2,600 m above sea level” – to tap into the premium market.
With the U.S. pet industry spending on natural treats, imported yak chews can command higher margins. A packaging expert found that a unique flavor or limited-edition yak chew can fetch a 42% profit margin compared to generic products. Importers should explore private labeling: working with a Nepali manufacturer to create exclusive recipes, flavors or sizes. As the pet packaging blog notes, “the brands winning right now combine all these elements – they’re not just selling dog chews, they’re selling an experience”.
U.S. importers should also watch for new channels: e-commerce sales of pet treats are booming (set to overtake retail by 2027). Private-label yak chew brands that optimize online marketing (clear windows, health claims, Himalayan images) can quickly carve out loyal audiences. In short, by partnering with certified Nepali exporters, U.S. companies can develop branded Himalayan yak chew lines – whether by sticking with the standard “white-label” products or investing in fully private-label R&D.
Import Checklist for the USA
To summarize, here are the key action steps for importing Himalayan dog chews:
- Supplier Verification: Confirm your Nepalese exporter has all certifications (ISO, HACCP, SA8000, DFTQC) and obtains a Veterinary Sanitary Certificate and DFTQC Test Report (quarantine release).
- FDA Registration: Ensure both the foreign processor and your U.S. facility are registered with FDA (Food Facility Registration). Obtain Unique Facility Identifiers (UFIs) for submission.
- Prior Notice: File prior notice with FDA (Bioterrorism Act) before each shipment.
- USDA/APHS Permit: Obtain an APHIS import permit for dairy-based pet food.
- Label Review: Have all labels reviewed for FDA compliance (21 CFR Part 501 and AAFCO guidelines). Include Guaranteed Analysis and feeding instructions.
- Documentation: Collect and prepare all export documents – Commercial Invoice, Packing List, COO, health certificate, test reports – and send copies to your customs broker.
- Tariff Code: Use HTS 2309.10.00.90 for dog/cat treats (duty-free).
- Shipping Plans: Decide on air or sea freight. Use temperature/humidity control (refrigeration or desiccants).
- Customs Entry: Work with a U.S. broker to file entry, CBP forms, and EPA regulations, if any. Provide all documentation.
- Testing: Before shipping, conduct heavy metal, microbiological, and nutrient tests. Keep COAs and lab reports.
- Ongoing Compliance: Maintain records (FSVP file, test results, supplier checks). Plan for annual updates of FDA registrations and testing.
By ticking off these steps, importers can significantly reduce delays and compliance risks.
Why Import Himalayan Yak Chews?
Global Demand & Market Size
The demand for natural pet treats has surged worldwide, and Himalayan yak chews are at the forefront of this growth. Nepal’s export position is well-documented: according to Kathmandu Post (citing Nepal Department of Customs): Nepal dog chew exports surged 27.82% in first half of 2024–25, Nepal exported 963 tonnes of dog chews worth NPR 1.80 billion in the first half of fiscal year 2024–25, with 852 tonnes (NPR 1.59 billion) absorbed by U.S. buyers alone. This growth reflects a strong shift in consumer preference toward safe, healthy, and eco-friendly alternatives to traditional pet chews. The sector’s long-run trajectory is positive: according to GMI Insights: global pet food and treats market at 6.1% CAGR through 2034, valued at $138.9 billion in 2024, the global pet food and treats market, valued at $138.9 billion in 2024, is forecast to expand at a 6.1% CAGR through 2034, signaling sustained, long-term opportunity for Himalayan yak chew importers.
Benefits vs. Rawhide & Synthetic Chews
Unlike rawhide chews, which are often treated with chemicals and can pose choking hazards, Himalayan yak chews are made from 100% natural yak and cow milk. They are rich in protein, calcium, and essential minerals, while being free from artificial preservatives. As Dr. Sarah Wooten, DVM, notes, “Chewing on firm, natural textures can support dental health while offering dogs a safer alternative to heavily processed chews.” The durability of yak chews also makes them long-lasting, offering hours of engagement for dogs of all sizes, which reduces the need for constant replacements.
Consumer Trends: Natural, Organic, Long-Lasting Treats
Today’s pet parents are increasingly mindful of what they feed their companions. Consumer preferences firmly favor natural products: according to Market Research Future 2025: 70% of pet owners globally willing to pay a premium for health-beneficial pet food products, 70% of pet owners are willing to pay a premium for health-beneficial food, helping drive the global natural pet food market from $4.37 billion in 2024 to a projected $10 billion by 2035, a market squarely dominated by products like Himalayan yak chews. It align perfectly with these demands, providing a sustainably sourced, long-lasting, and highly nutritious treat. This makes them a competitive product in the U.S. market, where pet owners are willing to pay a premium for quality and authenticity.
Conclusion
Importing Himalayan yak chews into the USA can be highly rewarding, given the booming market for natural pet treats. The key is partnership: work with a certified Nepalese exporter that understands U.S. rules. A reputable Nepali supplier will ensure strong quality controls (ISO/HACCP), handle export paperwork (DFTQC tests, vet certificates, COO), and help tailor labeling for the U.S. market. Meanwhile, importers should stay current on U.S. regulations (FDA, FSMA, USDA) and collaborate with customs brokers and food labs.
Following the guidelines above, the U.S. pet brands and distributors can tap into the rapidly growing demand for Himalayan dog chews. As one industry expert advises, make sure to “partner with an exporter who understands and complies with FDA and USDA regulations, maintains proper certifications, ensures accurate labeling and packaging, and manages shipping logistics effectively”. By doing so, you’ll unlock the potential of this premium pet product.For U.S. companies searching for a Himalayan dog chew supplier from Nepal, contact us at YforYak – we are a certified exporter ready to help you 10x your pet treat lineup with authentic, top-quality yak cheese chews. Start importing Nepal’s finest dog chews today and meet the growing demand of U.S. pet owners.
What makes Himalayan yak chews a high-demand product in the U.S. pet market?
Himalayan yak chews are made from 99% natural yak and cow milk, making them a clean-label, high-protein alternative to rawhide and synthetic chews. Over 70% of U.S. dog owners prefer natural or organic pet treats, and yak chews align perfectly with this growing consumer preference. With 68 million U.S. households owning dogs and the pet treat segment valued at $11–13 billion, demand for premium Himalayan chews continues to rise year over year.
Which U.S. federal agencies regulate the import of Himalayan yak chews?
The FDA governs all imported pet foods under the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act, requiring facility registration, prior notice, and FSVP compliance. The USDA’s Animal and Plant Health Inspection Service (APHIS) may require an import permit since yak chews are a dairy-based, animal-origin product from a foot-and-mouth risk country like Nepal. Importers must also comply with the Bioterrorism Act’s prior notice requirements and FSMA’s Foreign Supplier Verification Program (FSVP) to legally bring the product into the U.S.
What certifications should a Nepalese yak chew exporter have before shipping to the U.S.?
Reputable Nepalese exporters should hold ISO 22000 (Food Safety), ISO 9001 (Quality Management), HACCP certification, and SA8000 for ethical production standards. They must also pass inspections from Nepal’s Department of Food Technology & Quality Control (DFTQC) and obtain an export test report confirming microbial and contaminant compliance. These certifications give U.S. importers confidence in product safety and significantly reduce the risk of FDA detention at the border.
What labeling requirements must Himalayan yak chew packaging meet for the U.S. market?
Under 21 CFR Part 501 and AAFCO guidelines, every package must display the product name, intended species, net weight, ingredient list, and guaranteed analysis (minimum protein/fat, maximum fiber/moisture). Labels must also include feeding directions, calorie content, and the name and address of the manufacturer or U.S. distributor, using AAFCO-approved ingredient names throughout. Both U.S. customary and metric units are required, and net weight must appear prominently on the principal display panel.
How does an importer file FDA Prior Notice for a yak chew shipment?
The Prior Notice must be submitted electronically through the FDA’s FURLS system before the shipment arrives at a U.S. port of entry. For air shipments, notice must be filed at least 2 hours in advance; for sea shipments, at least 4 hours before arrival. Failure to file Prior Notice can result in the shipment being refused entry by the FDA, making it one of the most critical compliance steps in the import process.
What is the correct HTS tariff code for Himalayan yak chews, and are they subject to import duty?
Himalayan dog chews are classified under HTS code 2309.10.00.90, Prepared animal feed, and are generally duty-free when imported into the United States. A 2002 U.S. Customs ruling explicitly confirmed this classification and duty-free status for dog chews. However, importers are still required to pay a Merchandise Processing Fee (MPF) of approximately 0.3464% of the shipment value, with a minimum of $32.
What shipping method is best for importing yak chews from Nepal to the U.S.?
Sea freight is the most cost-effective option for large orders exceeding 8,000 kg, with costs ranging from $0.60–$5 per kg depending on volume, though transit time can take 4–6 weeks. Air freight is better suited for smaller or urgent shipments, typically costing $5–$15 per kg with a 1–3 day transit time. Regardless of the shipping method, moisture control is essential, silica gel packets, desiccants, and vacuum-sealed, high-barrier packaging help prevent mold during long transit.
What documents are required to clear Himalayan yak chews through U.S. Customs?
The core documents include a Commercial Invoice, Packing List, Certificate of Origin, Veterinary Health Certificate, and DFTQC Test Report from the Nepalese exporter. On the U.S. side, importers must submit FDA Prior Notice confirmation, CBP entry forms (3461/7501), and any applicable USDA APHIS import permit for dairy-based pet food. A licensed U.S. customs broker can handle the submission of all these documents to CBP and FDA, ensuring accuracy and timeliness to prevent delays.
What are the most common mistakes importers make when bringing yak chews into the U.S.?
The most frequent errors include missing or incomplete documentation, such as no FDA Prior Notice, absent APHIS permit, or lack of a DFTQC certificate, which can result in immediate shipment detention or refusal. Incorrect labeling, such as missing guaranteed analysis values or using non-AAFCO ingredient names, is another common violation that triggers FDA non-compliance. Skipping pre-export lab testing for pathogens, heavy metals, or mycotoxins is also a costly oversight, as a failed U.S. border test can lead to the destruction of an entire shipment.
What are the private label opportunities for U.S. companies importing Himalayan yak chews?
Many U.S. pet brands source yak chews from certified Nepalese manufacturers and repackage them under their own private-label branding, leveraging the “Himalayan origin” story as a premium marketing angle. Nepal’s yak chew exports have grown approximately 227% over five years, signaling a strong and expanding supply base capable of supporting custom product lines. With e-commerce pet treat sales projected to overtake retail by 2027, importers who develop branded yak chew lines with strong packaging and health-focused messaging are well-positioned to capture significant market share.







